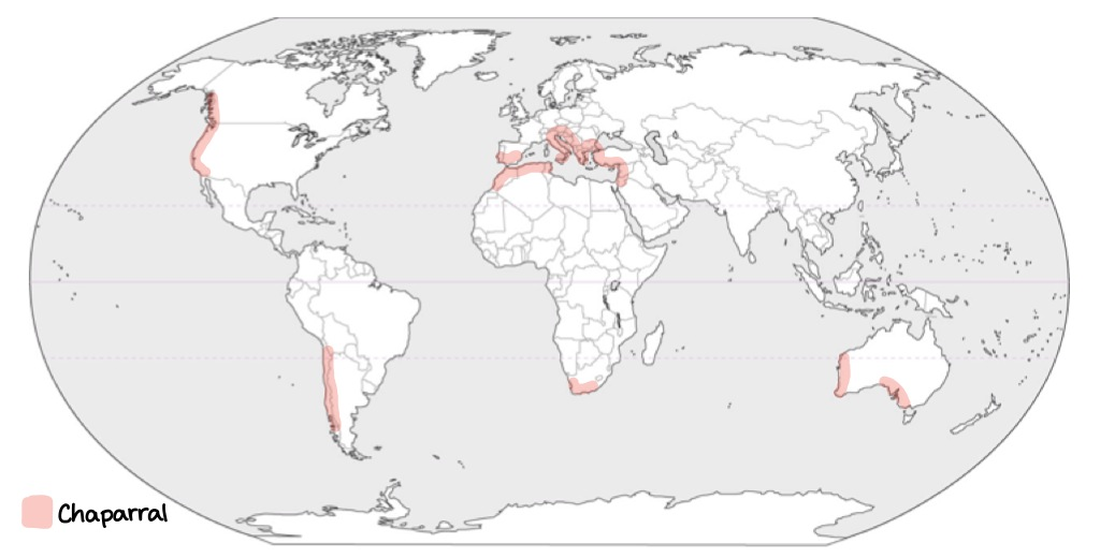
Chaparral is a distinct type of biome characterized by its dense, shrubby vegetation, often found in regions with a Mediterranean climate, which includes hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The plants in chaparral are typically drought-resistant and have adapted to withstand periodic wildfires, featuring thick, waxy leaves to minimize water loss. Common flora includes various species of sage, scrub oak, and manzanita, which provide crucial habitat for a variety of wildlife, including birds, small mammals, and reptiles. The soil in chaparral regions is often thin and nutrient-poor, contributing to the unique ecosystem dynamics. Overall, chaparral plays an essential role in maintaining biodiversity and preventing soil erosion in its often fragile environment.